Why Does My Hand Hurt? The Most Common Causes of Hand and Wrist Pain
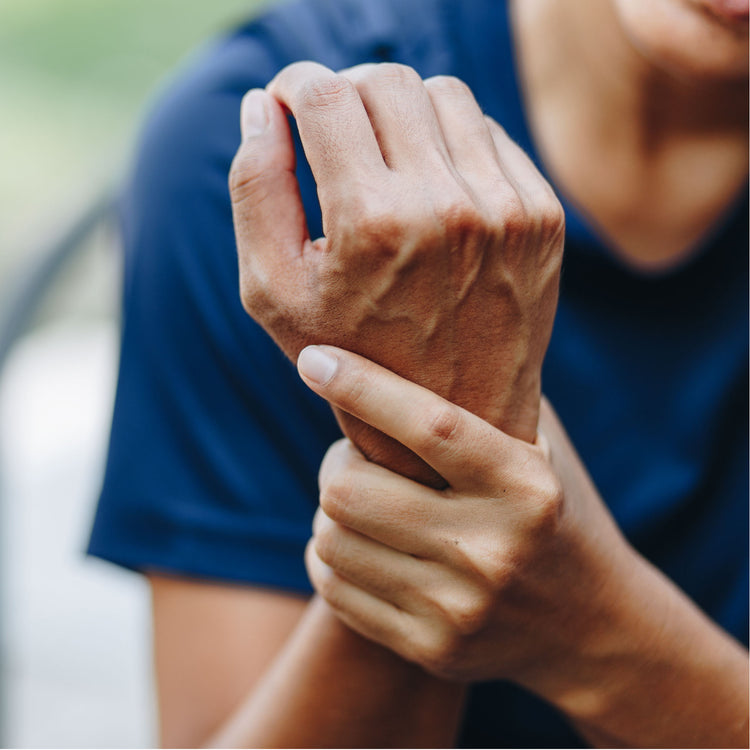

Wrist pain is a common condition that can affect people of all ages and lifestyles. It can be caused by a variety of factors, including injury, overuse, arthritis, and nerve damage. Wrist pain can significantly impact daily activities such as typing, gripping objects, or playing sports. It is important to identify the underlying cause of wrist pain in order to determine the appropriate treatment. Early intervention can help prevent further damage and promote healing. In this response, we will discuss the common causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options for wrist pain.
Injury:
Injuries such as sprains, strains, fractures, and dislocations can cause wrist pain. These injuries are often caused by falls, car accidents, or sports-related activities. A sprain occurs when the ligaments in the wrist are stretched or torn, while a strain occurs when the muscles or tendons in the wrist are stretched or torn. A fracture occurs when one or more of the bones in the wrist are broken, and a dislocation occurs when the bones in the wrist are forced out of their normal position.

Overuse:
Repetitive activities such as typing, using a mouse, or playing sports that involve the wrist can lead to overuse injuries such as tendonitis and carpal tunnel syndrome. Tendonitis is inflammation of the tendons in the wrist, while carpal tunnel syndrome occurs when the median nerve, which runs from the forearm to the hand, becomes compressed as it passes through the wrist. These conditions can cause pain, swelling, and stiffness in the wrist.

Arthritis:
Osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, and gout are types of arthritis that can affect the wrist and cause pain and stiffness. Osteoarthritis occurs when the cartilage that cushions the joints in the wrist breaks down, while rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune disorder that causes inflammation in the joints. Gout is a type of arthritis caused by a buildup of uric acid crystals in the joints.
Nerve damage:
Conditions such as carpal tunnel syndrome, cubital tunnel syndrome, and radial tunnel syndrome can cause nerve damage in the wrist and lead to pain and weakness. Carpal tunnel syndrome occurs when the median nerve is compressed as it passes through the carpal tunnel in the wrist. Cubital tunnel syndrome occurs when the ulnar nerve, which runs from the neck to the hand, becomes compressed as it passes through the elbow. Radial tunnel syndrome occurs when the radial nerve, which runs from the neck to the hand, becomes compressed as it passes through the forearm.
Symptoms of wrist pain can vary depending on the underlying cause of the pain. However, there are some common symptoms that people may experience, which are listed below:
Pain:
Pain is the most common symptom of wrist pain. The pain can range from mild to severe and can be described as aching, throbbing, sharp, or shooting. The pain may be constant or intermittent, and it may be worse with certain activities.
Swelling:
Swelling is another common symptom of wrist pain. It can be caused by injury, arthritis, or inflammation. The swelling may be localized to the wrist or may extend to the fingers or hand.
Stiffness:
Stiffness is a common symptom of wrist pain, especially in the morning or after a period of inactivity. The stiffness can make it difficult to move the wrist and may be accompanied by a sensation of tightness or discomfort.
Weakness:
Weakness is a less common symptom of wrist pain, but it can occur in some cases. Weakness may make it difficult to grip objects or perform certain activities that require wrist strength.
Numbness or Tingling:
Numbness or tingling in the wrist, hand, or fingers may occur with conditions such as carpal tunnel syndrome or nerve damage. These sensations may be accompanied by a feeling of weakness or a pins-and-needles sensation.
Redness or Warmth:
Redness or warmth around the wrist may indicate an infection or inflammation. These symptoms should be evaluated by a healthcare provider.
It is important to note that the severity of wrist pain symptoms can vary depending on the underlying cause and how long the pain has been present. In some cases, wrist pain may develop suddenly and be accompanied by significant swelling and redness, indicating an acute injury or infection. In other cases, the pain may be more gradual and develop over time, especially with overuse or degenerative conditions like arthritis.
Furthermore, the location of wrist pain can also vary depending on the underlying cause. For example, pain on the top of the wrist may indicate a ligament injury, while pain on the thumb side of the wrist may be a sign of De Quervain's tenosynovitis. Pain on the pinky side of the wrist may be a sign of ulnar-sided wrist pain, which can be caused by a variety of conditions such as triangular fibrocartilage complex (TFCC) tears or ulnar impaction syndrome.
It is also important to pay attention to any other accompanying symptoms, such as fever or signs of infection, as this may indicate a more serious condition that requires immediate medical attention.
Diagnosing wrist pain can be a complex process, as there are many potential causes of wrist pain, and the symptoms can overlap. However, with a thorough medical evaluation, diagnostic tests, and imaging studies, healthcare providers can determine the underlying cause of wrist pain and develop an effective treatment plan.
Here are some common diagnostic techniques that healthcare providers may use when evaluating wrist pain:
Physical Examination:
A physical examination is typically the first step in diagnosing wrist pain. The healthcare provider will examine the wrist and hand for signs of swelling, redness, warmth, or deformity. They may also test the range of motion and strength of the wrist and fingers, and assess for any signs of nerve damage.
Medical History:
The healthcare provider may ask about the history of the wrist pain, including when it started, what makes it better or worse, and any previous injuries or medical conditions. They may also ask about any other symptoms, such as numbness or tingling.
Diagnostic Tests:
Depending on the suspected cause of the wrist pain, the healthcare provider may order additional tests, such as blood tests or joint fluid analysis, to help diagnose an underlying medical condition or infection.
Imaging Studies:
Imaging studies, such as X-rays, CT scans, or MRIs, may be ordered to visualize the bones, ligaments, and soft tissues of the wrist and hand. These tests can help identify fractures, ligament injuries, or other structural abnormalities.
Nerve Conduction Studies:
In cases where nerve damage or carpal tunnel syndrome is suspected, nerve conduction studies may be performed to measure the electrical activity of the nerves in the wrist and hand.
In some cases, a diagnosis may require a combination of these diagnostic techniques. It is important to work with a qualified healthcare provider who can help determine the underlying cause of wrist pain and develop an effective treatment plan.
In conclusion, diagnosing wrist pain can be a complex process, requiring a combination of physical examination, medical history, diagnostic tests, and imaging studies. It is important to seek medical attention if you experience persistent or worsening wrist pain, as early diagnosis and treatment can help prevent further damage and promote healing.
The treatment for wrist pain will depend on the underlying cause of the pain, as well as the severity of the symptoms. In some cases, wrist pain can be treated with conservative measures, such as rest, ice, compression, and elevation (RICE). In more severe cases, medications, injections, or surgery may be required.
Here are some common treatments for wrist pain:
RICE:
Rest, ice, compression, and elevation can help reduce inflammation and pain associated with mild wrist injuries. Resting the wrist and avoiding activities that aggravate the pain can also help promote healing.
Medications:
Over-the-counter pain relievers, such as acetaminophen or nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), can help relieve pain and reduce inflammation. In some cases, prescription pain medications or muscle relaxants may be necessary.
Physical Therapy:
Physical therapy can help improve range of motion, strength, and flexibility of the wrist and hand. A physical therapist can also provide education on proper body mechanics and ergonomic techniques to prevent future injuries.
Injections:
Corticosteroid injections may be used to reduce inflammation and pain associated with conditions such as arthritis or tendinitis.
Surgery:
Surgery may be necessary for more severe cases of wrist pain, such as fractures, ligament tears, or nerve compression. The type of surgery will depend on the underlying cause of the pain and may involve arthroscopy, open reduction and internal fixation, or joint replacement.
It is important to work with a qualified healthcare provider to determine the most appropriate treatment plan for your wrist pain. Depending on the cause of the pain, a combination of these treatments may be necessary to achieve optimal results.
In addition to medical treatments, lifestyle modifications can also help prevent future wrist pain. This may include ergonomic adjustments to your work or home environment, stretching and strengthening exercises, and avoiding repetitive or high-impact activities that can strain the wrist and hand.
Wrist braces and compression sleeves are two types of medical devices that can be used to help relieve wrist pain. They work by providing support to the wrist joint and surrounding tissues, as well as helping to reduce inflammation and promote healing. Here's a closer look at how these devices can help with wrist pain:
Wrist Braces:
Wrist braces are typically made of a lightweight, breathable material that is designed to fit snugly around the wrist. They can be worn for extended periods of time, including during sleep and daily activities. There are several types of wrist braces available, including:
Resting wrist braces: These braces are designed to immobilize the wrist joint and prevent movement. They are typically used for injuries such as fractures or severe sprains, and are worn for a limited period of time.
Supportive wrist braces: These braces provide mild to moderate support to the wrist joint, and can be used for a variety of conditions, including arthritis, carpal tunnel syndrome, and tendonitis. They are typically worn during activities that may aggravate the pain.
Compression wrist braces: These braces provide both support and compression to the wrist joint and surrounding tissues. They can help reduce swelling and inflammation, and can be worn during activities or for extended periods of time.
Wrist braces can help with wrist pain by providing support to the joint and surrounding tissues, reducing movement and preventing further damage. They can also help improve blood flow and reduce inflammation, which can promote healing.
Compression Sleeves:
Compression sleeves are designed to fit snugly around the wrist and forearm, providing gentle pressure and support to the tissues. They are typically made of a stretchy, breathable material that is comfortable to wear for extended periods of time. There are several types of compression sleeves available, including:
Wrist compression sleeves: These sleeves are designed to provide compression to the wrist joint and surrounding tissues. They can help reduce swelling and inflammation, and may be used for conditions such as carpal tunnel syndrome, tendonitis, or arthritis.
Forearm compression sleeves: These sleeves provide compression to the muscles and tissues in the forearm, helping to improve blood flow and reduce fatigue. They may be used for conditions such as tennis elbow or golfer's elbow.
Compression sleeves can help with wrist pain by improving blood flow and reducing inflammation in the affected area. They can also provide support and stability to the tissues, helping to prevent further damage and promote healing.
Arthritis gloves:
Arthritis gloves are a type of therapeutic gloves that can be used to help alleviate hand pain and stiffness associated with arthritis. These gloves are designed to provide compression and support to the joints and muscles of the hand, which can help reduce inflammation, improve circulation, and promote healing. Here's how arthritis gloves can help with hand pain:
Compression:
Arthritis gloves are made of a stretchy, breathable material that is designed to fit snugly around the hand and fingers. The compression provided by the gloves helps to reduce swelling and inflammation in the affected joints, which can help alleviate pain and stiffness.
Support:
The gloves also provide support to the muscles and ligaments of the hand, helping to stabilize the joint and reduce the risk of further damage. The support provided by the gloves can also help improve hand function, allowing individuals to perform daily tasks with greater ease and comfort.
Warmth:
Arthritis gloves are often made of materials that provide warmth to the hands, such as neoprene or nylon. This warmth can help improve blood flow to the affected joints, which can promote healing and reduce pain.
Mobility:
Many arthritis gloves are designed with open fingertips, which allows for greater mobility and dexterity while wearing the gloves. This can be particularly helpful for individuals who need to perform fine motor tasks, such as typing or knitting, while experiencing hand pain.
Overall, wrist braces and compression sleeves can be effective tools for managing wrist pain. However, it is important to work with a healthcare provider to determine the most appropriate type of device for your specific condition, as well as the proper fit and duration of use. With proper use and care, wrist braces and compression sleeves can help improve wrist function and reduce pain, allowing individuals to resume their daily activities with greater ease and comfort. Here at Blitzugear.com, we offer an extensive selection of braces to meet your needs.
In conclusion, the treatment for wrist pain will depend on the underlying cause and severity of the pain. A combination of conservative measures, medications, injections, physical therapy, and surgery may be necessary to relieve pain and promote healing. Lifestyle modifications can also help prevent future wrist pain.
Wrist pain can be a common problem that can affect people of all ages and activity levels. It can be caused by a wide range of factors, including injury, overuse, arthritis, nerve compression, and medical conditions. Symptoms of wrist pain may include pain, stiffness, swelling, weakness, and numbness or tingling.
Diagnosing wrist pain can be a complex process, requiring a combination of physical examination, medical history, diagnostic tests, and imaging studies. Treatment for wrist pain will depend on the underlying cause and severity of the pain, and may include rest, medication, physical therapy, injections, or surgery.
It is important to seek medical attention if you experience persistent or worsening wrist pain, as early diagnosis and treatment can help prevent further damage and promote healing. Lifestyle modifications, such as ergonomic adjustments and stretching and strengthening exercises, can also help prevent future wrist pain.
Overall, proper diagnosis, treatment, and prevention are essential for managing wrist pain and maintaining wrist health. Working with a qualified healthcare provider and following a comprehensive treatment plan can help alleviate symptoms and improve quality of life.