The Most Common Causes and Treatments of Back Pain

Back pain is a prevalent health issue that affects millions of people globally, and it can strike anyone, regardless of age or fitness level. It can be a frustrating and debilitating condition, impacting daily activities such as sitting, standing, and even sleeping. The pain can range from mild to severe and can be constant or intermittent. For some individuals, back pain may go away on its own, while others may require medical intervention to manage their symptoms. With so many potential causes of back pain, it is crucial to understand the underlying factors that contribute to this condition. This knowledge can empower individuals to take preventative measures to reduce the risk of developing back pain or take appropriate action to manage their symptoms when they occur. So, let's dive deeper into the common causes of back pain and how to address them.

Poor Posture
Poor posture can cause back pain because it places unnecessary strain on the muscles and joints in the back, leading to discomfort and pain. When an individual maintains a slouched or hunched position, it puts additional pressure on the spinal discs and joints in the back, leading to misalignment and compression.
This can result in muscle strain, tension, and stiffness, as the muscles work harder to support the spine and maintain balance. Poor posture can also cause the muscles in the back to become weaker over time, making it more difficult to maintain proper alignment and posture in the future.
Furthermore, poor posture can also affect the alignment of the entire body, leading to additional issues such as hip or knee pain. For example, if an individual has a forward head posture, it can cause the shoulders to round forward, which can lead to a decrease in the space between the shoulders and the hips, causing the pelvis to tilt forward. This can result in lower back pain, hip pain, and even knee pain.
Therefore, it is essential to maintain good posture to reduce the risk of developing back pain. This includes sitting and standing up straight, with the shoulders relaxed and the spine in a neutral position. By practicing good posture, individuals can reduce the risk of back pain, improve their overall health, and maintain a pain-free lifestyle.
Poor posture can cause several symptoms, including:
Pain in the neck, shoulders, and upper back
Headaches
Stiffness or tension in the muscles
Fatigue or weakness in the muscles
Decreased flexibility and range of motion
Numbness or tingling in the arms or hands
Breathing difficulties due to compressed organs
Digestive problems, such as acid reflux or constipation
Poor balance or coordination
Reduced athletic performance.
Treatment for poor posture that causes back pain typically involves a combination of corrective exercises, lifestyle changes, and ergonomics. Here are some common treatments for poor posture:
Corrective exercises: Physical therapy and corrective exercises can help strengthen the muscles in the back, neck, and shoulders, improving posture and reducing pain. These exercises may include stretches, strength training, and posture-specific movements.
Lifestyle changes: Making simple lifestyle changes, such as standing up and walking around regularly during long periods of sitting, can help improve posture. Maintaining a healthy weight, getting enough sleep, and reducing stress can also improve posture.
Ergonomics: Proper ergonomics, such as using an ergonomic chair or adjusting the height of a computer monitor, can help reduce the strain on the back and neck caused by poor posture.
Chiropractic care: Chiropractic care may be beneficial for some individuals with poor posture. A chiropractor can perform adjustments to help realign the spine and improve posture.
Posture aids: Posture aids, such as braces, posture-correcting shirts, and ergonomic pillows, can provide additional support for the back and neck, helping to maintain proper posture.
It is important to address poor posture early on to prevent the development of chronic pain and other complications. With proper treatment and self-care, most cases of poor posture can be improved or corrected, leading to reduced pain and improved quality of life.
These symptoms may worsen over time if poor posture is not corrected. It is important to address poor posture early on to prevent the development of chronic pain and other complications.
Preventing back pain caused by poor posture involves making simple changes to your daily routine and environment. Here are some tips to help prevent back pain caused by poor posture:
Maintain good posture: Try to maintain good posture throughout the day, whether sitting, standing, or walking. Keep your shoulders back, chest up, and chin parallel to the ground.
Take breaks: Take breaks from sitting or standing for extended periods. If you sit for long periods, try to get up and move around every 30 minutes.
Exercise regularly: Exercise regularly to strengthen the muscles that support your back and maintain good posture. This can include stretching, strength training, and cardio exercises.
Use ergonomic furniture: Use ergonomic furniture, such as a supportive chair, to reduce the strain on your back and maintain good posture.
Adjust your work environment: Adjust your computer monitor and keyboard to the proper height and position to maintain good posture while working.
Use posture aids: Consider using posture aids, such as a lumbar roll or ergonomic pillow, to provide support and help maintain good posture.
Wear comfortable shoes: Wear comfortable shoes that provide proper support and cushioning for your feet and back.
By implementing these simple changes and maintaining good posture, you can help prevent back pain caused by poor posture. If you do experience back pain, seek medical advice to determine the cause and appropriate treatment.
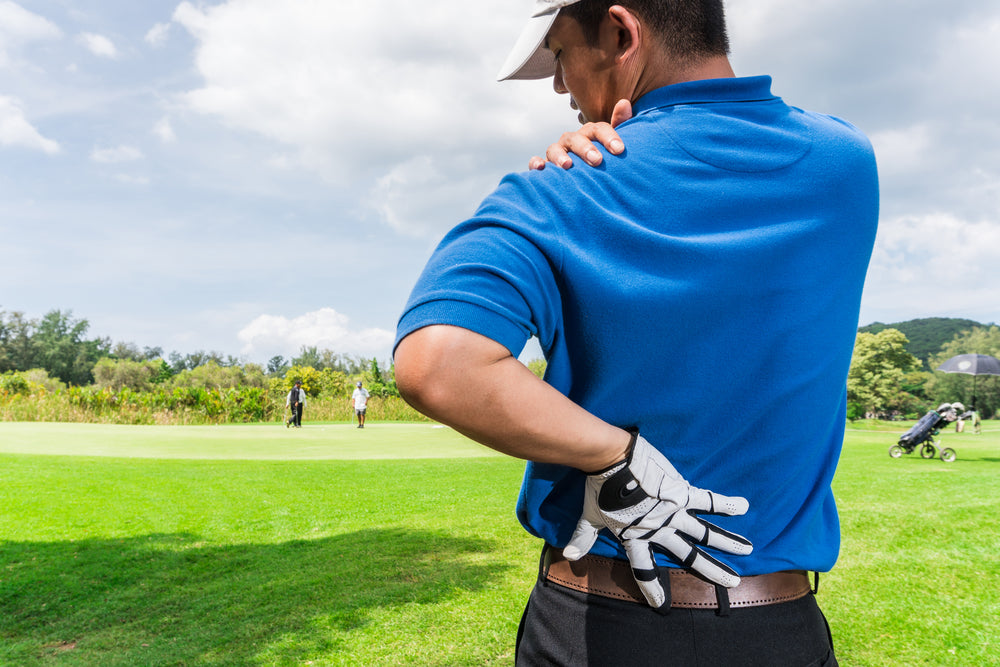

Muscle Strain
Muscle strain is a common cause of back pain, and it occurs when the muscles in the back become overstretched or torn. This can happen due to a sudden injury, such as lifting a heavy object or twisting the back, or from repetitive strain on the muscles, such as sitting in a hunched position for extended periods.
Muscle strain can cause back pain because it leads to inflammation, swelling, and pain in the affected area. When the muscles are strained, they can become weak, making it difficult to support the spine and maintain proper alignment. This can put additional strain on other muscles and joints in the back, leading to further pain and discomfort.
Muscle strain can also cause trigger points or "knots" in the affected muscles, which can refer pain to other areas of the back or even to other parts of the body, such as the neck or shoulders. These trigger points can be very tender to the touch and can cause significant pain and discomfort.
To treat muscle strain and back pain, it is essential to rest the affected area, apply ice or heat to reduce inflammation, and take over-the-counter pain relievers, such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen. Physical therapy or massage therapy can also be helpful in reducing pain and restoring proper function to the affected muscles.
Preventing muscle strain and back pain involves maintaining proper posture, avoiding heavy lifting or twisting motions, staying active with regular exercise, and taking frequent breaks when sitting or standing for extended periods. By taking these preventative measures, individuals can reduce the risk of muscle strain and back pain and maintain a healthy, pain-free back.
Muscle strain is a common cause of back pain, and it can cause a range of symptoms. The symptoms of muscle strain for back pain may include:
Pain in the affected area: Muscle strain can cause pain in the back, which may be dull or sharp.
Stiffness: The muscles in the affected area may feel stiff, making it difficult to move the back.
Swelling: In some cases, muscle strain can cause swelling in the affected area.
Muscle spasms: Muscle spasms can cause sudden, sharp pain in the back.
Limited range of motion: Muscle strain can make it difficult to move the back, leading to a limited range of motion.
Tenderness: The affected area may be tender to the touch.
Weakness: Muscle strain can cause weakness in the back muscles, making it difficult to perform daily activities.
The severity of the symptoms may vary depending on the extent of the muscle strain. If you experience any of these symptoms, it is important to seek medical advice to determine the cause and appropriate treatment for your back pain.
Treatment for muscle strain that causes back pain typically involves a combination of self-care measures and medical interventions. Here are some treatments for muscle strain for back pain:
Rest: Resting the affected area is important to allow the muscle to heal. Avoid any activities that exacerbate the pain.
Ice and heat therapy: Applying ice to the affected area can help reduce inflammation and pain, while applying heat can help promote blood flow and healing. Alternating between ice and heat therapy can be effective.
Over-the-counter pain relievers: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), such as ibuprofen or naproxen, can help reduce pain and inflammation.
Physical therapy: Physical therapy can help relieve pain, improve range of motion, and strengthen the muscles in the affected area.
Massage therapy: Massage therapy can help reduce muscle tension and relieve pain.
Muscle relaxants: In some cases, muscle relaxants may be prescribed to help relieve muscle spasms and pain.
Injections: Corticosteroid injections can be administered to the affected area to help reduce inflammation and pain.
Surgery: Surgery may be required in severe cases where the muscle strain has caused significant damage to the spine.
It is important to consult with a healthcare provider to determine the appropriate treatment for your back pain caused by muscle strain. In addition to treatment, preventive measures such as maintaining good posture and stretching regularly can also help prevent muscle strain and reduce the risk of back pain.
Preventing back muscle strain involves taking care of your back and adopting healthy habits that reduce the risk of injury. Here are some tips for preventing back muscle strain:
Maintain good posture: Keeping your back straight and avoiding slouching or hunching can reduce the risk of muscle strain.
Stretching: Regular stretching, especially before engaging in physical activities, can help warm up the muscles and reduce the risk of muscle strain.
Strengthening exercises: Strengthening exercises, such as core strengthening exercises, can help improve the stability and strength of your back muscles.
Avoid lifting heavy objects: Lifting heavy objects can strain your back muscles. If you must lift something heavy, bend your knees and lift with your legs, not your back, also wear a back brace to support and protect your back.
Wear proper shoes: Wearing shoes with good support can help reduce the strain on your back muscles.
Take breaks: Taking regular breaks during prolonged periods of sitting or standing can help prevent muscle strain.
Maintain a healthy weight: Excess weight can put additional strain on your back muscles.
Quit smoking: Smoking can reduce blood flow to your muscles, including your back muscles, increasing the risk of muscle strain.
By adopting these preventive measures, you can reduce the risk of back muscle strain and prevent back pain. However, if you experience any symptoms of back pain, it is important to seek medical attention to determine the cause and appropriate treatment.

Herniated or bulging discs
Herniated or bulging discs are a common cause of back pain, particularly in the lower back region. These discs act as cushions between the vertebrae in the spine, helping to absorb shock and allow for smooth movement of the spine.
When a disc herniates or bulges, it means that the tough outer layer of the disc has become weakened, allowing the soft inner material to protrude outwards. This can put pressure on nearby nerves in the spinal cord, leading to pain, numbness, and tingling sensations in the back, legs, or arms.
Herniated or bulging discs can also cause back pain due to inflammation and irritation of the surrounding tissue. The body's natural response to the injury is to send immune cells to the affected area, which can cause swelling and pain.
The severity of back pain caused by herniated or bulging discs can vary depending on the location and severity of the injury. Some individuals may experience mild discomfort, while others may have severe, debilitating pain that interferes with daily activities.
Treatment for herniated or bulging discs typically involves rest, pain management, and physical therapy to strengthen the muscles in the back and improve flexibility. In more severe cases, surgery may be necessary to repair or remove the affected disc.
Preventing herniated or bulging discs involves maintaining a healthy weight, practicing good posture, lifting heavy objects correctly, and avoiding repetitive motions that put undue strain on the back. By taking these preventative measures, individuals can reduce the risk of developing herniated or bulging discs and maintain a healthy, pain-free back.
Herniated or bulging discs can cause a variety of symptoms, depending on the location and severity of the condition. Here are some common symptoms of herniated or bulging discs:
Pain: The most common symptom of a herniated or bulging disc is pain in the affected area, which can range from mild to severe. The pain may be localized to the back or radiate to other areas, such as the legs, arms, or neck.
Numbness or tingling: Herniated or bulging discs can compress nerves in the affected area, causing numbness or tingling sensations. This is especially common in the arms or legs.
Weakness: Herniated or bulging discs can also cause weakness in the affected area, making it difficult to perform certain movements or tasks.
Loss of reflexes: In severe cases, herniated or bulging discs can cause a loss of reflexes in the affected area.
Difficulty standing or sitting: Herniated or bulging discs can make it difficult to sit or stand for prolonged periods of time, and can cause discomfort during movement.
Bowel or bladder problems: In rare cases, herniated or bulging discs can compress nerves that control bowel or bladder function, leading to incontinence or difficulty with bowel movements.
If you experience any of these symptoms, it is important to seek medical attention to determine the cause and appropriate treatment for your herniated or bulging disc.
The treatment for herniated or bulging discs depends on the severity of the condition and the symptoms experienced by the patient. Here are some common treatments for herniated or bulging discs:
Pain medication: Over-the-counter pain medication, such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen, can help relieve pain associated with herniated or bulging discs.
Physical therapy: Physical therapy can help strengthen the muscles in the affected area and improve flexibility and range of motion.
Epidural steroid injections: Injections of corticosteroids can help reduce inflammation and relieve pain associated with herniated or bulging discs.
Surgery: In severe cases, surgery may be necessary to remove the herniated or bulging disc and relieve pressure on the nerves.
Chiropractic care: Chiropractic adjustments can help realign the spine and alleviate pressure on the nerves. Wear a brace can also help with the pain.
Acupuncture: Acupuncture involves the insertion of thin needles into specific points on the body to help relieve pain and promote healing.
It is important to note that not all cases of herniated or bulging discs require medical intervention, and conservative treatments such as rest, ice, and heat therapy may be sufficient to manage symptoms. However, it is important to seek medical attention if you experience persistent or severe symptoms, or if your symptoms are affecting your quality of life.
While herniated or bulging discs can occur due to a variety of factors, there are some preventive measures you can take to reduce your risk of developing this condition:
Maintain good posture: Poor posture can place unnecessary stress on your spine and increase your risk of herniated or bulging discs. Be mindful of your posture when sitting, standing, and lifting heavy objects.
Exercise regularly: Regular exercise can help strengthen the muscles in your back and abdomen, which can help support your spine and reduce your risk of herniated or bulging discs.
Lift heavy objects properly: When lifting heavy objects, use your legs and keep your back straight. Avoid twisting or bending at the waist when lifting heavy objects.
Quit smoking: Smoking can impair the delivery of nutrients to your spinal discs, increasing your risk of herniated or bulging discs.
Maintain a healthy weight: Excess weight can place added stress on your spine and increase your risk of herniated or bulging discs.
Practice proper ergonomics: If you work at a desk or perform repetitive tasks, make sure your workstation is ergonomically designed to minimize strain on your back and neck.
By incorporating these preventive measures into your daily routine, you can reduce your risk of developing herniated or bulging discs and maintain a healthy spine.

Arthritis
Arthritis is a common cause of back pain, particularly in older individuals. Arthritis is a condition that causes inflammation and stiffness in the joints, leading to pain and discomfort.
When arthritis affects the spine, it can cause pain in the back, neck, or hips. Arthritis in the spine can be caused by a variety of factors, including wear and tear on the joints, injuries, or autoimmune disorders that attack the joints.
Arthritis can cause back pain because it leads to inflammation in the joints, which can make it difficult to move and bend the spine. This can result in stiffness and pain in the affected area, making it difficult to perform daily activities.
In some cases, arthritis can also cause the formation of bone spurs, which are small bony growths that develop around the affected joints. These bone spurs can put pressure on nearby nerves in the spinal cord, leading to additional pain and discomfort.
Treatment for arthritis-related back pain typically involves managing pain with over-the-counter or prescription pain relievers, such as ibuprofen or corticosteroids. Physical therapy or exercise can also be helpful in reducing pain and improving mobility in the affected area. In some cases, surgery may be necessary to remove bone spurs or replace damaged joints.
Preventing arthritis-related back pain involves maintaining a healthy weight, staying active with regular exercise, and avoiding activities that put undue strain on the back. By taking these preventative measures, individuals can reduce the risk of developing arthritis and maintain a healthy, pain-free back.
Arthritis in the back can cause a variety of symptoms, including:
Pain: Arthritis can cause chronic pain in the back, which may be felt as a dull ache or a sharp, stabbing pain.
Stiffness: Arthritis can cause stiffness and limited range of motion in the back, making it difficult to perform daily activities.
Swelling: Arthritis can cause inflammation and swelling in the back, which can further contribute to pain and stiffness.
Tenderness: The affected area may be tender to the touch.
Tingling or numbness: Arthritis in the back can put pressure on nerves, causing tingling or numbness in the arms, legs, or other parts of the body.
Weakness: Arthritis can weaken the muscles in the back, making it difficult to support the spine and maintain proper posture.
It is important to note that symptoms of arthritis in the back can vary depending on the type and severity of the condition. If you are experiencing persistent or severe symptoms, it is important to seek medical attention to receive an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
Treatment for arthritis in the back typically involves a combination of medication, physical therapy, and lifestyle changes. Here are some common treatments for arthritis in the back:
Medications: Over-the-counter pain relievers such as acetaminophen or nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) can help manage pain and inflammation. In some cases, prescription medications may be necessary.
Physical therapy: A physical therapist can design exercises to help improve mobility, flexibility, and strength in the back. This can help alleviate pain and improve function.
Heat and cold therapy: Applying heat or cold to the affected area can help reduce pain and inflammation.
Lifestyle changes: Maintaining a healthy weight, avoiding activities that exacerbate symptoms, and practicing good posture can help reduce stress on the back and improve overall function.
Surgery: In severe cases, surgery may be necessary to remove damaged tissue or replace a damaged joint.
It's important to consult with a healthcare professional for a personalized treatment plan. They can help determine the most appropriate course of action based on the type and severity of arthritis you have, as well as any other medical conditions you may have.
While there is no surefire way to prevent arthritis in the back, there are steps you can take to reduce your risk or delay the onset of the condition. Here are some prevention tips for arthritis in the back:
Maintain a healthy weight: Carrying extra weight puts added stress on the joints, which can increase the risk of arthritis. Maintaining a healthy weight through regular exercise and a healthy diet can help reduce this risk.
Exercise regularly: Exercise can help strengthen the muscles and improve flexibility, which can help protect the joints. Low-impact exercises like swimming, walking, or yoga can be especially beneficial for the back.
Practice good posture: Poor posture can place extra stress on the back, which can increase the risk of arthritis. Maintaining good posture while sitting, standing, and lifting can help reduce this risk.
Protect your back: Avoiding activities that place excessive stress on the back, such as heavy lifting or high-impact exercise, can help reduce the risk of injury and arthritis.
Avoid smoking: Smoking has been linked to an increased risk of arthritis, so avoiding or quitting smoking can help reduce this risk.
Get regular check-ups: Regular check-ups with a healthcare professional can help identify any potential issues early on and provide treatment before they progress.
It's important to note that while these prevention tips can help reduce the risk of arthritis in the back, they do not guarantee prevention. It's important to consult with a healthcare professional for personalized advice and treatment.
Spinal stenosis is a condition that occurs when the spinal canal narrows, putting pressure on the spinal cord and nearby nerves. This narrowing can be caused by a variety of factors, including age-related degeneration of the spine, spinal injuries, or bone spurs that develop around the affected area.
Spinal stenosis can cause back pain because it puts pressure on the spinal cord and nerves, leading to pain, numbness, or tingling sensations in the back, legs, or arms. The severity of the pain can vary depending on the location and extent of the narrowing.
In addition to pain, spinal stenosis can also cause weakness in the affected area, making it difficult to move or perform daily activities. In severe cases, spinal stenosis can lead to loss of bladder or bowel control, which requires immediate medical attention.
Treatment for spinal stenosis typically involves managing pain with over-the-counter or prescription pain relievers, such as ibuprofen or corticosteroids. Physical therapy or exercise can also be helpful in reducing pain and improving mobility in the affected area. In more severe cases, surgery may be necessary to remove the affected tissue or to fuse the affected vertebrae.
Preventing spinal stenosis involves maintaining a healthy weight, staying active with regular exercise, and avoiding activities that put undue strain on the back. By taking these preventative measures, individuals can reduce the risk of developing spinal stenosis and maintain a healthy, pain-free back.
Spinal stenosis occurs when the spinal canal narrows, which can put pressure on the nerves and cause a range of symptoms. Here are some common symptoms of spinal stenosis:
Back pain: Spinal stenosis can cause chronic back pain, which may be dull or sharp and can worsen over time.
Numbness or tingling: Pressure on the nerves can cause numbness or tingling in the legs, buttocks, or feet.
Weakness: Spinal stenosis can cause weakness or a loss of muscle control in the legs, which can lead to difficulty walking or standing.
Cramping or pain in the legs: Some people with spinal stenosis may experience cramping or pain in the legs, especially during activity.
Bowel or bladder problems: In rare cases, spinal stenosis can cause bowel or bladder dysfunction, which requires immediate medical attention.
It's important to note that some people with spinal stenosis may not experience any symptoms, while others may experience severe symptoms. If you're experiencing any of these symptoms, it's important to consult with a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and treatment plan.
The treatment for spinal stenosis depends on the severity of the symptoms and the underlying cause of the condition. Here are some common treatment options:
Physical therapy: Physical therapy can help improve strength, flexibility, and balance, which can help alleviate symptoms.
Medications: Over-the-counter pain relievers such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen may help reduce pain and inflammation. Prescription medications, such as muscle relaxants or nerve pain medications, may also be prescribed.
Injections: Corticosteroid injections can help reduce inflammation and relieve pain.
Surgery: If the symptoms are severe and conservative treatments are not effective, surgery may be recommended. Surgery for spinal stenosis involves decompression of the affected nerves or spinal cord.
It's important to note that spinal stenosis is a chronic condition that may require ongoing treatment to manage symptoms. A healthcare professional can help determine the best course of treatment based on the individual's specific needs and circumstances.
It's not always possible to prevent spinal stenosis, as it can be caused by a variety of factors, including age-related changes in the spine, genetics, or injury. However, there are some steps that may help reduce the risk of developing spinal stenosis or slow the progression of the condition:
Maintain good posture: Poor posture can put extra pressure on the spine, which can contribute to spinal stenosis. Maintaining good posture can help reduce this pressure.
Exercise regularly: Regular exercise can help keep the spine flexible and strong, which may help prevent spinal stenosis or slow its progression.
Maintain a healthy weight: Excess weight can put extra pressure on the spine, which can contribute to spinal stenosis. Maintaining a healthy weight can help reduce this pressure.
Avoid repetitive motions: Repeatedly performing the same motions, such as twisting or bending, can put extra stress on the spine, which can contribute to spinal stenosis.
Avoiding these motions or taking frequent breaks can help reduce this stress.
Seek prompt treatment for injuries: Injuries to the spine, such as fractures or dislocations, can increase the risk of developing spinal stenosis. Seeking prompt treatment for these injuries can help reduce this risk.
It's important to note that these steps may not prevent spinal stenosis entirely, but they may help reduce the risk of developing the condition or slow its progression.

Osteoporosis
Osteoporosis is a condition that causes bones to become weak and brittle, making them more susceptible to fractures and breaks. When osteoporosis affects the spine, it can lead to compression fractures, which can cause severe back pain.
Compression fractures occur when a vertebra in the spine collapses or fractures under pressure, causing the affected bone to lose height. This can cause the spine to curve or become misaligned, leading to pain and discomfort in the affected area.
Osteoporosis can cause back pain because it weakens the bones in the spine, making them more susceptible to compression fractures. These fractures can occur due to everyday activities, such as bending or lifting, or from a fall or trauma.
Treatment for osteoporosis-related back pain typically involves managing pain with over-the-counter or prescription pain relievers, such as ibuprofen or opioids. Physical therapy or exercise can also be helpful in reducing pain and improving mobility in the affected area. In some cases, surgery may be necessary to repair or stabilize the affected vertebrae.
Preventing osteoporosis-related back pain involves maintaining a healthy diet rich in calcium and vitamin D, staying active with regular exercise, and avoiding activities that put undue strain on the back. By taking these preventative measures and treating osteoporosis early, individuals can reduce the risk of developing compression fractures and maintain a healthy, pain-free back.
Osteoporosis is a condition in which the bones become weak and brittle, increasing the risk of fractures. In the early stages of osteoporosis, there may be no symptoms. However, as the condition progresses, the following symptoms may occur:
Back pain: Osteoporosis can cause small fractures in the spine, which can lead to back pain.
Loss of height: As osteoporosis progresses, the bones in the spine can become compressed, causing a loss of height.
Stooped posture: The compression of the spine can also cause a stooped posture or a hump in the upper back.
Bone fractures: Osteoporosis increases the risk of bone fractures, especially in the wrist, hip, and spine.
It's important to note that these symptoms can also be caused by other conditions, so it's important to consult a healthcare professional if any of these symptoms occur. Additionally, osteoporosis can be diagnosed with a bone density test, so regular screenings may be recommended for individuals at risk.
There are several treatment options available for osteoporosis, including:
Medications: There are several medications available that can help prevent bone loss and increase bone density. Some examples include bisphosphonates, hormone therapy, and selective estrogen receptor modulators (SERMs).
Calcium and Vitamin D supplements: Calcium and Vitamin D are essential for bone health, and supplements may be recommended to ensure adequate intake.
Exercise: Weight-bearing exercises such as walking, jogging, and strength training can help improve bone density and reduce the risk of fractures.
Fall prevention: Falls can increase the risk of fractures in individuals with osteoporosis, so it's important to take steps to prevent falls, such as removing tripping hazards, using assistive devices, and practicing balance exercises.
Lifestyle changes: Smoking and excessive alcohol consumption can increase the risk of osteoporosis, so quitting smoking and limiting alcohol intake may also be recommended.
Treatment for osteoporosis should be individualized based on the individual's age, overall health, and the severity of their condition. It's important to work with a healthcare professional to determine the best treatment plan.
There are several steps individuals can take to help prevent osteoporosis, including:
Getting enough calcium and Vitamin D: Adequate calcium and Vitamin D intake is essential for bone health. Good sources of calcium include dairy products, leafy greens, and fortified foods. Vitamin D can be obtained from sunlight exposure, fatty fish, and fortified foods.
Regular exercise: Weight-bearing exercises such as walking, jogging, and strength training can help improve bone density and reduce the risk of fractures.
Quit smoking: Smoking can increase the risk of osteoporosis, so quitting smoking is important for maintaining bone health.
Limit alcohol intake: Excessive alcohol consumption can increase the risk of osteoporosis, so limiting alcohol intake is recommended.
Fall prevention: Falls can increase the risk of fractures in individuals with osteoporosis, so taking steps to prevent falls, such as removing tripping hazards, using assistive devices, and practicing balance exercises, is important.
Bone density testing: Regular bone density testing can help identify individuals who are at risk of osteoporosis and allow for early intervention.
It's important to note that not all cases of osteoporosis can be prevented, especially in cases where there is a genetic predisposition or underlying medical condition. However, taking steps to maintain bone health can help reduce the risk of developing osteoporosis and related complications.

Skeletal irregularities
Skeletal irregularities refer to any structural abnormalities in the spine, such as scoliosis (a sideways curvature of the spine) or kyphosis (an exaggerated curvature of the upper back). These irregularities can cause back pain by putting additional pressure on the spine and surrounding muscles, ligaments, and nerves.
Skeletal irregularities can cause back pain because they can affect the natural alignment and curvature of the spine. This can lead to muscle imbalances and tension, as the muscles surrounding the affected area try to compensate for the irregularity. Over time, this tension can cause pain, stiffness, and discomfort in the affected area.
In addition to pain, skeletal irregularities can also cause mobility issues, making it difficult to move or perform daily activities. In severe cases, skeletal irregularities can also lead to nerve compression, which can cause additional pain and discomfort.
Treatment for back pain related to skeletal irregularities typically involves physical therapy or exercise to improve posture and strengthen the muscles surrounding the affected area. In some cases, bracing or surgery may be necessary to correct the structural irregularity.
Preventing back pain related to skeletal irregularities involves maintaining a healthy weight, staying active with regular exercise, and practicing good posture habits, such as sitting up straight and avoiding slouching. By taking these preventative measures, individuals can reduce the risk of developing skeletal irregularities and maintain a healthy, pain-free back.
Skeletal irregularities can cause various symptoms in the back, including:
Back pain: This may be a dull ache or sharp pain that worsens with movement.
Postural problems: Skeletal irregularities can cause changes in posture, such as a hunched or curved spine.
Limited range of motion: Certain skeletal irregularities can limit the range of motion in the back, making it difficult to perform certain activities.
Muscle spasms: The muscles in the back may spasm in response to skeletal irregularities, causing pain and discomfort.
Numbness or tingling: In some cases, skeletal irregularities can compress the nerves in the back, leading to numbness or tingling in the legs or feet.
The specific symptoms of skeletal irregularities can vary depending on the type and severity of the condition. It's important to seek medical evaluation if you experience any persistent back pain or related symptoms.
The treatment options for skeletal irregularities depend on the type and severity of the condition. Here are some common treatments:
Physical therapy: A physical therapist can develop an exercise program to help improve posture and strengthen the muscles of the back.
Pain medication: Over-the-counter pain medications like acetaminophen or nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) can help relieve mild to moderate back pain.
Braces or supports: Depending on the type of skeletal irregularity, a brace or support may be recommended to help improve posture and support the spine.
Surgery: In severe cases, surgery may be necessary to correct skeletal irregularities. This is typically only recommended if other treatments have not been effective.
Lifestyle changes: Certain lifestyle changes, such as maintaining a healthy weight and avoiding activities that put excessive strain on the back, can help manage back pain caused by skeletal irregularities.
It's important to consult with a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment plan for your specific condition.
While some skeletal irregularities are congenital or caused by conditions such as scoliosis, there are some steps you can take to prevent skeletal irregularities from developing or worsening. Here are some prevention tips:
Maintain good posture: Proper posture is important for maintaining a healthy spine. Make sure to sit and stand up straight, and avoid slouching or hunching over.
Exercise regularly: Exercise can help strengthen the muscles in your back and improve posture. Aim for 30 minutes of moderate exercise most days of the week.
Practice safe lifting techniques: When lifting heavy objects, use your legs to lift, not your back. Avoid twisting your back when lifting.
Maintain a healthy weight: Excess weight can put strain on your back, so maintaining a healthy weight can help prevent skeletal irregularities from developing.
Avoid prolonged periods of inactivity: Sitting or standing for long periods of time can put strain on your back, so take breaks and move around regularly.
Wear supportive shoes: Shoes with good arch support can help promote proper posture and reduce strain on the back.
By incorporating these prevention tips into your daily routine, you can help reduce your risk of developing skeletal irregularities or worsening existing conditions.

Infections
There are several causes of back infections, including:
Bacterial or viral infections: These types of infections can spread to the bones, muscles, or soft tissues of the back, causing inflammation and pain. Bacterial infections can occur due to medical procedures, such as spinal injections or surgeries, or from infections in other parts of the body that spread to the spine. Viral infections, such as shingles, can also cause back pain.
Urinary tract infections: In some cases, urinary tract infections (UTIs) can spread to the kidneys, causing kidney infections that can result in back pain.
Soft tissue infections: Infections in the muscles or soft tissues of the back can occur due to injuries, such as cuts or puncture wounds, or from underlying medical conditions, such as diabetes.
Fungal infections: Fungal infections, such as histoplasmosis or aspergillosis, can cause back pain when they affect the bones of the spine.
Tuberculosis: Tuberculosis (TB) is a bacterial infection that can affect the spine, causing a condition known as spinal TB. This can lead to severe back pain and even spinal deformities if left untreated.
Back infections can cause a range of symptoms, which may vary depending on the specific type and severity of the infection. Some common symptoms of back infections include:
Pain: Back infections can cause severe pain in the affected area. The pain may be localized or spread to other areas of the back or body.
Fever: A fever is a common symptom of back infections, as the body tries to fight off the infection.
Swelling: Infections can cause swelling and inflammation in the affected area.
Redness: In some cases, the skin around the infected area may appear red or discolored.
Stiffness: Back infections can cause stiffness and reduced range of motion in the affected area.
Fatigue: Feeling tired and weak is a common symptom of back infections, as the body expends energy fighting the infection.
Numbness or tingling: If the infection affects the nerves in the back, it may cause numbness, tingling, or weakness in the legs or other areas of the body.
If you experience any of these symptoms, it's important to seek medical attention right away, as back infections can be serious and require prompt treatment.
The treatment for back infections will depend on the type and severity of the infection. In general, treatment may involve a combination of antibiotics, pain relief, and supportive measures to help manage symptoms and promote healing.
Antibiotics: If the infection is bacterial in nature, antibiotics may be prescribed to help clear the infection. It's important to take antibiotics exactly as prescribed and for the full course of treatment, even if symptoms improve.
Pain relief: Back infections can be very painful, and pain relief medications such as acetaminophen or ibuprofen may be recommended to help manage pain and reduce inflammation.
Rest: Resting and avoiding activities that exacerbate symptoms can help to promote healing and prevent further damage to the affected area.
Supportive measures: Depending on the specific symptoms and type of infection, supportive measures such as physical therapy, hot or cold compresses, or drainage of fluid may be recommended to help manage symptoms and promote healing.
In some cases, surgery may be necessary to drain an abscess or remove infected tissue. It's important to seek prompt medical attention if you suspect you have a back infection, as delay in treatment can lead to serious complications.
Back infections prevention involves taking measures to reduce the risk of developing an infection in the back or spine. Here are some ways to prevent back infections:
Good hygiene: Wash your hands regularly and avoid touching your face to prevent the spread of bacteria and viruses that can cause infections.
Proper wound care: If you have a wound or incision in your back, follow your doctor's instructions for wound care. Keep the area clean and dry, change dressings as directed, and report any signs of infection, such as redness, swelling, or drainage.
Proper nutrition: Eating a healthy and balanced diet can help boost your immune system, which can help your body fight off infections.
Regular exercise: Regular exercise can help strengthen your back muscles, improve your posture, and reduce your risk of back injuries that can lead to infections.
Proper lifting techniques: When lifting heavy objects, use proper lifting techniques to avoid straining your back muscles or causing injury.
Avoid smoking: Smoking can weaken your immune system and increase your risk of infection.
Avoid risky behaviors: Avoid risky behaviors that can increase your risk of infection, such as sharing needles or having unprotected sex.
Get vaccinated: Talk to your doctor about vaccinations that can help protect you from infections, such as tetanus and flu.

Medical conditions
There are several medical conditions that can cause back pain, including:
Arthritis: Arthritis is a condition that causes inflammation and stiffness in the joints. When it affects the joints in the back, it can cause pain, stiffness, and limited mobility.
Osteoporosis: Osteoporosis is a condition that causes the bones to become weak and brittle, which can lead to fractures or compression fractures in the spine, resulting in severe back pain.
Fibromyalgia: Fibromyalgia is a chronic pain disorder that can cause widespread pain and tenderness throughout the body, including the back.
Scoliosis: Scoliosis is a condition where the spine curves to one side, causing uneven pressure on the discs and joints in the back, which can lead to pain and discomfort.
Herniated or bulging discs: When the soft, gel-like material inside a spinal disc pushes through a tear in the outer layer, it can press on nearby nerves, causing pain and discomfort in the back.
Spinal stenosis: Spinal stenosis is a condition where the spinal canal narrows, putting pressure on the nerves in the back and causing pain, numbness, and tingling.
Infections: Infections can cause inflammation and pain in the bones, muscles, and soft tissues of the back, leading to back pain.
Cancer: Certain types of cancer, such as bone cancer or cancer that has spread to the spine, can cause severe back pain.
Lower back pain is a common condition that affects people of all ages and can have a significant impact on daily activities. There are several possible causes of lower back pain, including poor posture, muscle strain, herniated discs, and spinal stenosis. While lower back pain can be uncomfortable and disruptive, it is often treatable with a combination of rest, physical therapy, medication, and lifestyle changes.
Preventive measures such as maintaining good posture, regular exercise, and avoiding activities that may cause strain or injury to the back can help reduce the risk of lower back pain. It's important to seek medical attention if the pain is severe, lasts for a long time, or is accompanied by other symptoms such as numbness or tingling in the legs.

In conclusion, lower back pain can be a challenging condition to manage, but with the right treatment approach, most people can find relief and resume their normal activities. It's essential to take proactive steps to prevent lower back pain and seek professional medical advice when necessary.
Many different types of injuries and conditions can be relieved by our orthopedic braces. An orthopedic brace is used to provide targeted support and compression to an injured area, resulting in reduced inflammation, improved circulation, and stabilized joints or muscles, all of which may help to alleviate pain and improve mobility. Blitzu well-designed orthopedic brace can be used to provide comfort and support to customers who suffer from chronic conditions such as arthritis or recently suffered an injury such as sprained ankles or torn ligaments to help them return to their daily activities with less discomfort and pain.